Difference between road traffic and rail traffic
Basic understanding and philosophy of rail transport
Road traffic
This article is about the basic understanding and philosophy of how a control program works in general and TrainController in particular.
- Model railroader Silvio Richter describes this in the forum as follows:
In contrast to road traffic, where drivers drive by sight and pay attention themselves and traffic lights are timed, rail traffic works somewhat differently.
Rail transport
The engine driver drives according to signals and the train dispatcher ensures route safety and sets the switches and signals.
So if a signal shows a movement aspect, then it is also ensured at the same time that there is no other train on the released route. Routes are only reserved for trains if a movement order has been issued.
No enemy sidings
In terms of TrainController, this means that blocks are pre-reserved and switch routes are only activated when a corresponding train journey requires them.
It is therefore not possible to activate enemy routes in TrainController.
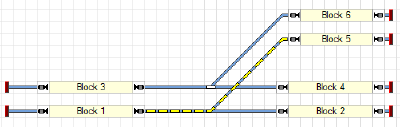
Intersection as an example
Abb: Fahrweg reservieren
Eine Fahrt vom Block 4 nach Block 3 ist nur dann möglich, wenn keine aktive Fahrt vom Block 1 nach Block 5 stattfindet. Die aktive Weichenstraße 1<->5 verhindert das Aktivieren der Weichenstraße 3<->4. Es bleibt das Signal im Block 4 bei einer aktiven Zugfahrt solange rot, bis der Weg von Block 1 nach Block 5 freigegeben wird.
Weblinks
Quelle: Forum
- -- Uslex (Diskussion) 08:01, 31. Jul. 2023 (UTC)